Location
Adana, Türkiye
Key Partners
Lead: TEMSA CIRCESUITE5BETTLEI
Main Solutions
Data exchange, handling and interoperabilityInnovative inverters for storage systems and electric vehicles (V2G) Optimal management of the grid Optimal market selection
Description
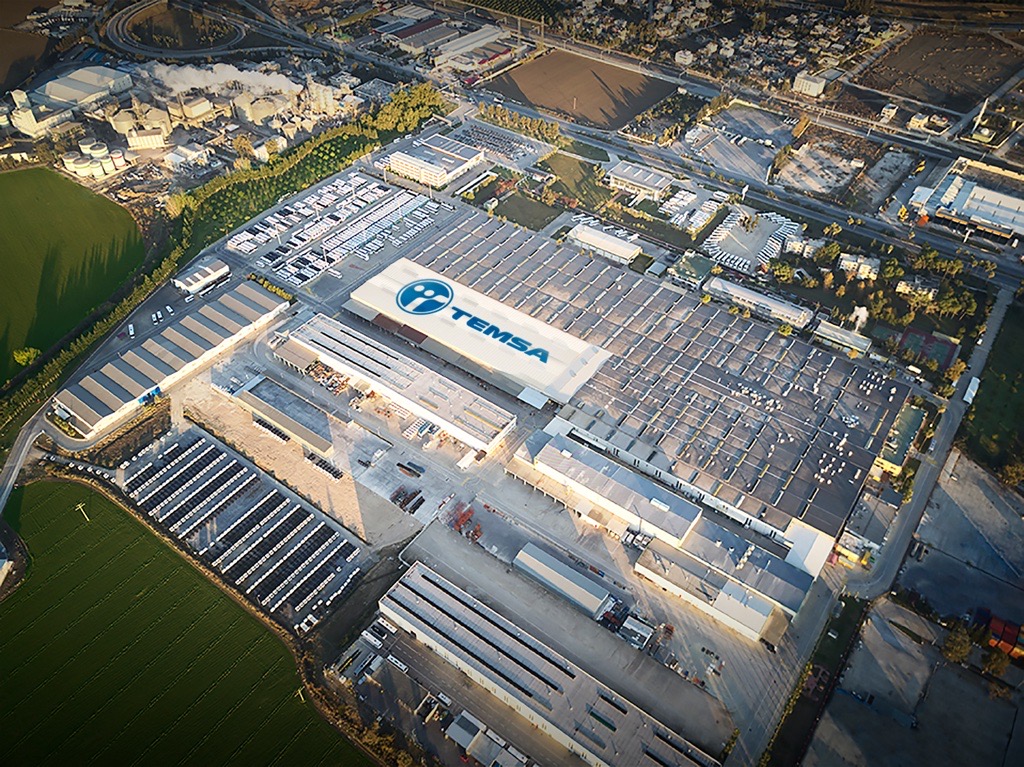
TEMSA, based in Türkiye, stands as a prominent player in the global bus and midibus manufacturing sector, with a widespread presenceinternationally. TEMSA’s contribution to the REEFLEX project involves the utilization of their installations situated in the Adana plant, covering an expansive area of 9,500 m2, inclusive of a substantial 4,500 m2 office building housing over 175 employees. Already slated for implementation alongside the REEFLEX project is the installation of a photovoltaic (PV) system with a capacity of 860 kW. This forward-thinking move aligns with TEMSA’s commitment to innovation and sustainability within their operations.
Currently, TEMSA employs an energy management system within their facilities, catering to both office spaces and manufacturing units, which monitors energy consumption patterns and alerts stakeholders about potential peaks. Furthermore, the presence of electric vehicle (EV) charging stations underscores TEMSA’s tendency toward environmentally conscious practices. However, the energy consumption of these stations remains untracked.
In this pilot, here’s a summary of what will be executed,
- Integration of REEFLEX innovations into TEMSA’s existing energy management system.
- Optimization of energy operation at a local level within TEMSA’s facilities.
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of the PV system and EV charging stations as primary flexibility assets.
- Tracking and optimization of energy demands across various devices using sensors and concentrators, including HVAC systems.
- Assessment of the impact of the implemented solutions on energy efficiency and cost savings.
- Testing the scalability and replicability of the REEFLEX platform in the context of the Turkish grid and automotive industry.
- Monitoring the performance of the pilot to identify opportunities for further enhancements and refinements.
Innovations and Technological Advances
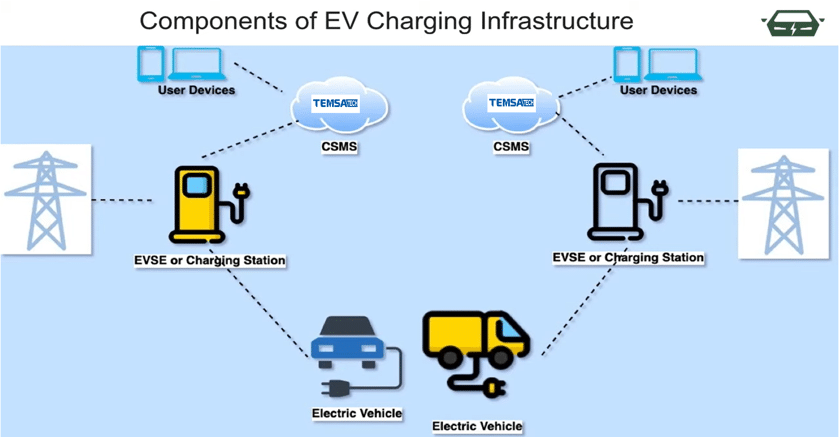
TemsaTech Central Management System (TTCM) allows EV charging industry players to monitor and optimize the charging of electric fleets using real-time data from chargers and vehicles.
REEFLEX will step on the already validated SYNERGY H2020 (part of the BRIDGEinitiative) Reference Big Data Platform Implementation and will properly extend and configure it to effectively address distributed data management for data assets flowing from residential premises and a variety of digitalised DERs, also enabling their flexibility managements through their integration with storage systems.
VERIFY LCA/LCC modelling toolkit will serve as the basis to perform relevant environmental analysis in the selected demonstrators. It will be integrated in the REEFLEX platform, and i) will be used to assess in almost near real-time the expected benefits from the synergetic operation of multiple grid assets (e.g., BESS, V2G charging stations) in the selected demo sites, and ii) will be linked with flexibility calculation algorithms and aggregation/disaggregation algorithms, developed within REEFLEX, to support cluster participation providing both environmental and economic benefits by grouping together prosumers with same needs and characteristics.
USE platform will be reconfigured to be integrated into the REEFLEX platform and applied for the scope of this project. More specifically: a) it will be upgraded to support the inclusion of new key performance indicators to be defined for REEFLEX; b) new threshold values and weights will be assigned, oriented to integrated energy systems, better reflecting country specific challenges. Measuring and monitoring performance will be supported by two main types of indicators and indices: a) simple concrete output indicators for monitoring the progress and effectiveness of the demonstration activities (e.g., % RES penetration, energy surplus); and b) impact-oriented indicators for assessing benefits of interventions (e.g., air quality improvement level, GHG savings). This will also help selected demo districts to perform self-assessments and benchmark their performance in meeting SDGs.
REEFLEX will extend and complement the concept of SRI by adapting it to flexibility providing devices to: (i) classify these devices according to their characteristics to provide flexibility to the system; (ii) generate, populate and update in the future a commonly agreed catalogue of energy smart home appliances; (iii) develop a protocol by which every manageable element provides a basic description from a flexibility point of view; (iv) develop a flexibility classification algorithm.
REEFLEX will develop a device with modular configuration that allows the solution to be scaled to the power required for each application. Each charging system consists of 25-kW AC/DC and 12.5- kW DC/DC bidirectional modules. The DC/DC modules provides high-frequency galvanic isolation to allow a safe operation and the series connection of modules, to achieve a higher output voltage range, and its parallel connection to achieve higher charging and discharging power.
REEFLEX platform will be able to operate with service providers that optimally manage their customers' flexible resources running algorithms on the common REEFLEX cloud, on proprietary clouds or on local gateways. The project will develop, evaluate and debug a set of algorithms for optimal operation and the application of flexibility set points that can be run on the edge, on proprietary clouds or on the central REEFLEX platform.
REEFLEX platform will be in charge of the interaction with the flexibility markets. It will be based on an advanced estimation of the expected behaviour of the market, both day-ahead and reserve/ancillary services ones. The first relies on price-oriented decision, while the second must consider supplementary data sources (e.g., weather forecasts) and demand/generation predictions.

Contact Information
Demo Site Leader: Nihan CIN, nihan.cin@temsa.com
Demo Site Leader proxy: Biran Can TURE, birancan.ture@temsa.com



Replicators
-
Denmark
Holbæk Municipality is a local government situated 60 km west of Copenhagen, in Zealand. Holbæk Municipality covers 578 square kilometers, has 72,000 inhabitants, and employs 4,500 persons. This replicator will involve between 10,000 and 15,000 consumers. These are mostly private consumers, owners of electric cars and Holbæk Municipality’s own electric cars. It aims to establish approximately 150 charging stations in Holbæk Municipality area and all necessary activities will be carried out to have the electricity grid installed, started, and put in operation. The internal unit “Green Transition and Sustainability” of Holbæk Municipality will be responsible for the coordination of this REEFLEX site and will internally act in a close cooperation with citizens, utilities, and associations for this replicator. The Municipality will await the 4 lighthouse demos in the project, and which must be reconciled with the planned roll-out of charging stations in Holbæk Municipality.
-
Portugal
Living Energy consists of a network of living-buildings, which are equipped with meters and sensors, connected to a cloud-based digital platform, in which a variety of building types, energy sources, load profiles and occupancy are collected from these living-buildings. Moreover, the living-buildings are monitored and with the user engagement it is possible to better understand how people use energy and their preferences in real-life.